Have you ever seen images of Saturn’s icy moon Enceladus, with its distinctive fractured surface? Nicknamed “tiger stripes”, these curious markings stretch across the south pole unlike anything else in the Solar System. But what could cause such striking surface features like Enceladus Tiger Stripes?
In this article, we will explore the mysteries behind Enceladus’ iconic tiger stripe markings. What natural processes shape this alien landscape carved in ice? What hidden mechanisms drive the strange activity emerging from within these cracks?
Dive below to discover what scientists are uncovering about Enceladus’ subsurface ocean. What role could this ocean play in the ongoing changes to the remarkable tiger stripes?
Read on to learn more about the puzzles yet to be solved regarding the tiger stripes of Enceladus.
Enceladus Tiger Stripes
What are the Enceladus tiger stripes? The Enceladus tiger stripes are long, icy fractures on the surface of Saturn’s moon Enceladus. They are named for their resemblance to tiger stripes. They are notable for spewing out water vapor and icy particles from beneath the moon’s icy crust.
These geysers suggest the presence of a subsurface ocean on Enceladus. Making it an intriguing target for scientists studying the potential for life beyond Earth.
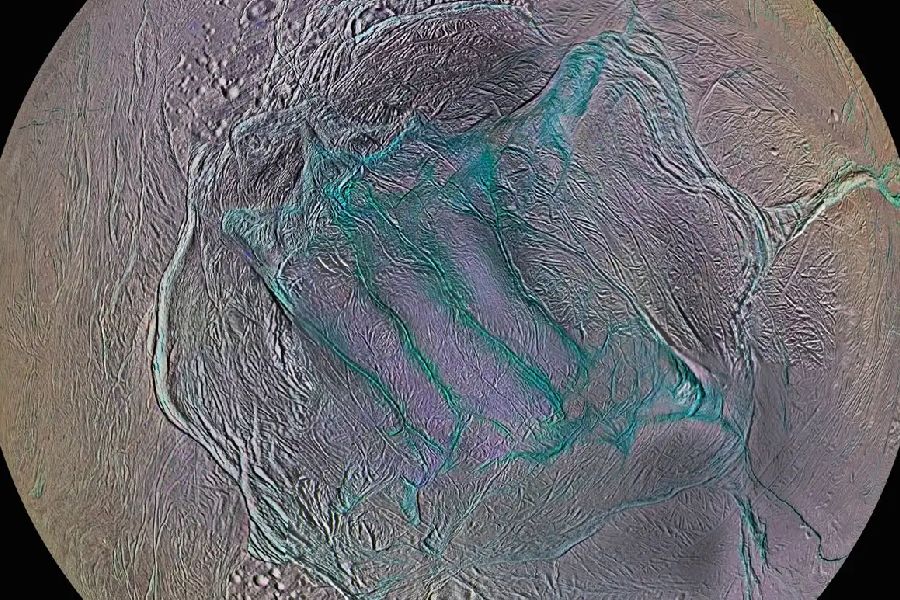
Characteristics of the Tiger Stripes
The four tiger stripes stretch uniquely across Enceladus’ south pole, standing out as deep, dark fractures against the icy terrain. When examining what geologic features are the tiger stripes on Enceladus, these markings stand out as exceptional crest-like formations – in contrast to other more chaotic terrain features across Saturn’s innermost moon.
The crevice-like markings extend around 18 miles below the surface. They exhibit higher heat, spewing water vapor and ice particles, and display gradual temperature changes and new fractures over the years. This indicates active internal processes that slowly evolve the stripes over time.
This distinct and visually striking formation reveals ongoing geological activity shaping the landscape of Saturn’s icy moon. The tiger stripes vary from 1-3 miles in width, but reach far deeper than surrounding fractures – evidence of the complex mechanisms driving their continued formation.
Multiple observations show the tiger stripes are truly exceptional markings on Enceladus’ surface that change notably across years, unlike anything else seen in the Saturn system.
Their active spewing of vapor amid a continuously evolving fractured terrain makes the iconic tiger stripes a mysterious formation still revealing its secrets.
Distinctive stripes
The four tiger stripes uniquely stretch straight across Enceladus’ south pole in orderly, parallel lines. This distinct shape already sets them apart from the moon’s chaotic surface fractures.
Additionally, the stripes cut incredibly deep into the ice – over 18 miles down, far deeper than nearby cracks. Their long, straight morphology is orderly relative to the jumbled surface terrain, while also penetrating much further through the icy crust.
The stripes also exhibit odd water compositions and excess heat output, unlike other surface features. Their visual uniqueness, extreme depth, abnormal chemistry, and heating distinguish the tiger stripes as special formations. The tiger stripes are shaped by complex inner forces within Enceladus.
Parallel fractures and cracks
The tiger stripes contain many smaller parallel cracks within them. These mini-fractures share similar compositions with the main stripes, indicating a related origin. Additional parallel cracks slowly generate over time along the stripes.
This ongoing formation suggests internal stress builds up, gradually splitting the tiger stripes into parallel pieces. As these fractures widen, more subsurface fluid likely rises and vents along the stripes. The parallel cracks seem to facilitate this constant renewal of geological activity in the tiger stripes.
Liquid water jets
The discovery of eruptive plumes was revelatory – liquid water actually flows inside Enceladus. Over 400 pounds vent each second, suggesting vast hidden oceans. Different jet signatures indicate complex subsurface processes uniquely shape distinct fractures.
The tiger stripes thus fundamentally changed our understanding – Enceladus’ alien interior actively churns today. Tracking plume changes reveals shifting deep conditions over time. The iconic geysers serve as crucial windows into the dynamic world hidden below the ice shell.
Tidal stresses
Saturn’s gravitational forces stretch and flex Enceladus’ interior. This tidal stress focuses intense cracking at the south pole over time, eventually forming the deep tiger stripes. The stripes match regions of peak tidal forces on the surface.
Even now, regular tides from orbit drive ongoing heating and activity within the fractures, preventing sealing. The tiger stripes start and persist thanks to celestial dynamics. Saturn’s pull enables the iconic cracks to remain active surface windows above the churning ocean below.
Origin of the Tiger Stripes
Scientists have competing theories for the stripes’ origin. Internal stress or comet impacts may have contributed some initial fracturing. However, evidence best supports intense heating and ice thinning producing the cracks.
Warm spots below likely enabled tidal forces over time to split the ice shell into the distinct stripes. This neatly explains their direct interactions with subsurface activity. Additional research is still needed, but warming and melting from Enceladus’ interior seems to have carved these unique surface windows we observe today.
Conclusion
We hope this exploration of the Enceladus tiger stripes has illuminated some of the mysteries surrounding these iconic surface fractures. This article has traced their distinctive characteristics, likely formation mechanisms and complex ongoing changes that offer a window into the moon’s hidden oceans.
While questions remain around their exact origins, it’s clear the tiger stripes provide a gateway to studying the dynamic alien processes occurring in Enceladus’ warm core. As we discover more via future missions like the Enceladus Orbilander we may unlock additional secrets of how the iconic Enceladus tiger stripes came to be and evolve over time.
For now, we have seen how these remarkable markings help reveal the geological story of Saturn’s active, icy moon. The tiger stripes showcase a tiny world brimming with scientific potential across the Solar System and beyond.
