Our awe-inspiring universe contains billions of galaxies, each with countless stars, planets, and other celestial wonders. Yet strange observations indicate the space between galaxies appears to be continuously expanding over time. But is the Universe expanding as these cosmic measurements suggest?
In this article, we will objectively investigate an enduring idea proposed in the 1920s – that the Universe itself is expanding. We provide background on this theoretical concept from famous astronomer Edwin Hubble.
Does observational evidence truly support that galaxies are racing away from each other? Or could other phenomena mimic the appearance of universal expansion instead? As we probe this captivating mystery that impacts models of cosmic origins, you may find your fundamental grasp of celestial distances transformed.
By exploring all facets of this puzzle, including arguments against the mainstream view, you can decide for yourself about the scope and scale of our reality. Join us on a journey through mind-bending ideas at the cutting edge of cosmology.
Is the Universe Expanding?
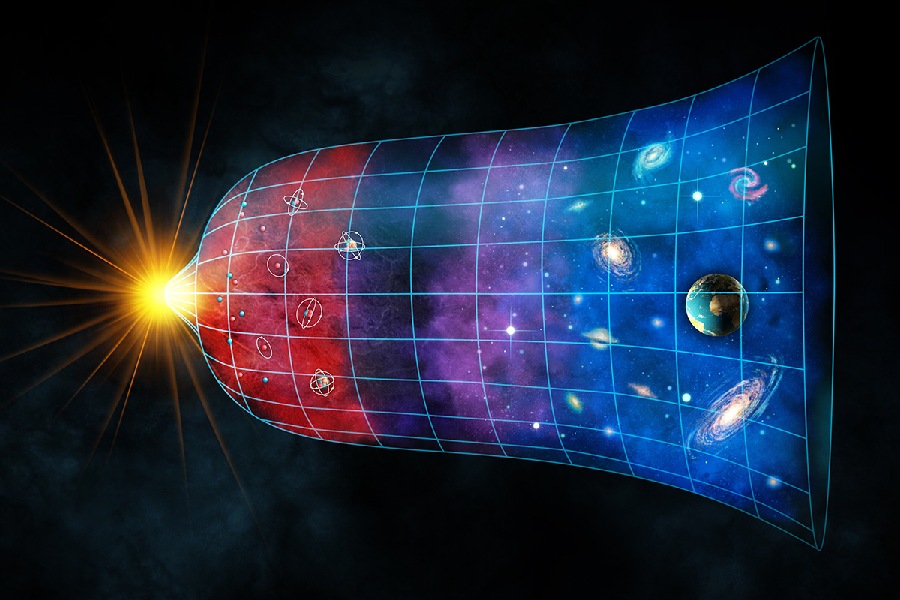
So, is the universe expanding? Yes, the universe is expanding. This concept, known as the expansion of the universe, is a fundamental aspect of modern cosmology.
Observations of distant galaxies and the discovery of cosmic microwave background radiation support the idea that galaxies are moving away from each other over time. This expansion suggests that the Universe had a beginning in a hot and dense state, commonly referred to as the Big Bang, and has been expanding ever since.
The evidence for the expanding universe has led to the development of the widely accepted cosmological model known as the Big Bang theory.
Foundation of the Expansion Theory
Explanation of Expansion Theory
The expansion theory proposes that the Universe is continuously spreading outward over time. It does not expand into anything, but rather, it stretches the fabric of space-time itself. Expansion occurs evenly between galaxies as space-time enlarges. Under this model, all galaxies drift farther apart.
The rate of expansion is estimated by measuring galaxies’ recessional velocities as they move away from us. Mathematical models extrapolate the universe’s size back in time to an infinitely hot and dense beginning point – the Big Bang. Expansion has been ongoing since this initial cosmic creation event over 13 billion years ago.
Historical background
In the 1920s, astronomer Edwin Hubble analyzed light from distant galaxies. He discovered that nearly all galaxies showed a “redshift,” indicating they were moving away from us. The farther the galaxy, the faster the recessional speed. This revelation meant the Universe was not static but expanding in all directions.
Hubble originally thought the galaxies were moving through space. Later refinements determined space-time itself was stretching between galaxies to drive them apart. How do we know space is expanding?
Hubble’s astonishing empirical evidence for universal expansion formed a cornerstone of the modern Big Bang theory. It kickstarted deductive cosmology to explain expansion’s newly-discovered origins.
Measurement and Quantification
Hubble’s Constant
The rate of universal expansion is quantified through Hubble’s constant, coined for Edwin Hubble’s foundational observations. This value measures how fast galaxies recede from us depending on their distances.
Current measurements set Hubble’s constant at about 67.4 km/s/Mpc – indicating that for every megaparsec farther out a galaxy is, its velocity increases by 67.4 km/s.
On cosmic scales, this constant allows extrapolating back to the dense, fiery beginnings at the Big Bang’s inception. Hubble’s value reduces uncertainties about the Universe’s age, size, and development. NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has helped refine accuracy to within 5%.
Expansion rate over time
If the universe is expanding, another important question staring at us is how fast is the universe expanding. Given a Hubble constant of 67 km/s/Mpc, experts estimate the universe grows by about 1.513% every 10 million years.
On shorter timescales, this percentage translates to an expansion of 74 kilometers per second. Daily expansion exceeds 6.4 million kilometers per day. These figures illustrate the continual, smooth enlargement of space-time between all galaxies across the observable universe.

Accelerating Expansion
Recent discoveries
Surprisingly, observations in the late 1990s first indicated that universal expansion was accelerating. Instead of slowing due to gravity over billions of years, the expansion rate is actually speeding up.
This acceleration was discovered by studying distant supernovae light curves and cosmic background radiation patterns. The finding shocked the scientific community and forced a re-evaluation of physics models.
Follow-up observations across expanding patches confirmed the initial evidence wasn’t anomalous. Independent tests further reinforce the perplexing reality that cosmic enlargement presently expands faster and faster rather than slowing.
Role of dark energy
Even though it was established that the Universe is expanding, the cause of this expansion has remained unknown. Why does the Universe expand? One theory seems quite promising.
The cause of accelerating expansion remains mysterious but is attributed to dark energy– an unknown form with strong repulsive gravity. Dark energy is theorized to permeate space-time itself uniformly.
As the universe enlarges, more dark energy inserts itself to stretch space-time even faster. This unusual energy, counteracting normal gravity, now drives 75% of cosmic expansion velocity.
Dark energy exhibits bizarre connections to the vacuum itself through quantum fluctuations that grow as the universe inflates. This quintessence energy resists dilution, causing its relative strength to increase over time as expansion continues endlessly into an exponentially stranger future cosmos.
The Nature of Infinite Expansion
Exploring the paradox
Universal expansion projections lead to an apparent paradox– if galaxies continuously drift apart, at some point, would not the universe become cold and empty? Cosmologists posit that while expansion is infinite, the current accelerating rate driven by dark energy will prevent this ultimate freezing.
Infinite expansion means the Universe has no theoretical limit or “edge” to its size over time. More space-time simply comes into existence to separate galaxies flying apart. Counterintuitively, the increasing volume produces effects assisting star and planet formation for trillions of years to come through gravitation.
Future of Cosmic Expansion
Speculation on the end of expansion
While prevailing theories strongly indicate infinite expansion, some conjecture cosmic enlargement may one day halt or collapse. Potential endings include the Big Crunch model, where expansion reverses to contraction.
However, current accelerating data rejects this scenario. All evidence points to galaxies eternally drifting apart even as their internal stars perish.
Alternative speculation suggests dark energy driving accelerating cosmic expansion may one day dissipate, causing expansion to approach uniform coasting gradually. But no mechanisms indicate cosmic acceleration switching off any time in the remote near future.
Predictions based on current understanding
The favored modern prediction is heat death in 100 trillion years as stars exhaust fuel sources. Although expansion continues infinitely, creating new space, declining matter density and temperature equilibrate at near-absolute zero.
Energy gradients driving complexity dissipate. Some black holes and atomic particles may still interact unless proton decay intervenes.
By this point, all stars, including red dwarfs, will have been extinguished. Black holes will dominate remnants as the cosmos becomes eternally dark and cold, with only decaying particles and weak black hole mergers occurring in unimaginably long stretches.
Implications for humanity
The inevitability of infinite universal expansion has profound implications for humanity’s cosmic future. Our epoch’s observable Universe forms an isolated “island” disconnected from regions expanding away faster than light speed allows communication.
This forms an effective horizon past which no beings can interact or gain information. Developing faster-than-light travel could perhaps permit contact with other civilizations also embedded in remote cosmic islands.
Attempting intergalactic communication or travel, even aided by warp drives, remains profoundly challenging. The feasibility requires not just immense technological gains. It also requires multigenerational ships or genetically engineered successors.
Conclusion
So, is the Universe expanding? After reviewing the historical and modern evidence, we can definitively conclude that the Universe is expanding and even accelerating in its epic enlargement.
From Hubble’s initial observations of galactic redshifts to recent supernova data, the case for an inflating cosmos is airtight. Dark energy’s repulsive gravity drives space-time itself to stretch ever faster, approaching infinitude.
Current and future NASA missions tracking expansion aim to refine predictions for the universe’s estimated 100 trillion-year maximum lifespan.
